MX9 UART
This page is using the default release mx93-yocto-kirkstone-5.15.71_2.2.0-v1.0.
To view this page for a specific Variscite SoM and software release, please follow these steps:
- Visit variwiki.com
- Select your SoM
- Select the software release
UART Overview
UART Overview - VAR-SOM-MX93
The VAR-SOM-MX93 and DART-MX93 expose up to seven LPUART interfaces, some of which are multiplexed with other peripherals.
| Serial Port | Device Node | Device Tree | VAR-SOM-MX93 / Symphony Board | DART-MX93 / DT8MCustomBoard |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UART0 | /dev/ttyLP0 | lpuart1 | Symphony board serial console | DT8MCustomboard serial console |
| UART2 | /dev/ttyLP2 | lpuart3 | Disabled by default, see datasheet | Disabled by default, see datasheet |
| UART3 | /dev/ttyLP3 | lpuart4 | Disabled by default, see datasheet | Disabled by default, see datasheet |
| UART4 | /dev/ttyLP4 | lpuart5 | 1.8V Signal level, used on SOM for Bluetooth interface and can be accessible only if Bluetooth is disabled.[1] | 1.8V Signal level, used on SOM for Bluetooth interface and can be accessible only if Bluetooth is disabled.[1] |
| UART5 | /dev/ttyLP5 | lpuart6 | Connected to Symphony board J18.7 and J18.9 | Connected to DT8MCustomboard J12.4 and J12.6 |
| UART6 | /dev/ttyLP6 | lpuart7 | Connected to Symphony board J18.3 and J18.5 | Connected to DT8MCustomboard J12.11 and J12.13 |
| UART7 | /dev/ttyLP7 | lpuart8 | Disabled by default, see datasheet | Disabled by default, see datasheet |
Disabling Bluetooth / Enabling UART4 (/dev/ttyLP4)
UART4/ttyLP4 is used by the Bluetooth on the SOM. To use it on the carrier, Bluetooth must be disabled on the SOM.
First, disable variscite-bt by running:
# systemctl stop variscite-bt; systemctl stop variscite-ot # systemctl disable variscite-bt; systemctl disable variscite-ot
Then, disable bluetooth in the device tree imx93-var-som.dtsi or imx93-var-dart.dtsi:
&lpuart5 {
...
bluetooth {
compatible = "nxp,88w8987-bt";
status = "disabled";
};
...
};
Testing UART5
The following demonstrates how to test UART5 on the VAR-SOM-MX93 Symphony board. The same process applies to the DT8MCustomboard following the table above.
Short J18.7 and J18.9 pins and run the following commands:
# stty -F /dev/ttyLP5 -echo -onlcr 115200 # cat /dev/ttyLP5 & # echo hello > /dev/ttyLP5
For each invocation of echo command the "hello" string should appear on the terminal.
Testing UART6
The following demonstrates how to test UART6 on the VAR-SOM-MX93 / Symphony board. The same process applies to the DT8MCustomboard following the table above.
Short J18.3 and J18.5 pins and run the following commands:
# stty -F /dev/ttyLP6 -echo -onlcr 115200 # cat /dev/ttyLP6 & # echo hello > /dev/ttyLP6
For each invocation of echo command the "hello" string should appear on the terminal.
Disabling UART5
To disable UART5 edit arch/arm64/boot/dts/freescale/imx93-var-som-symphony.dts or arch/arm64/boot/dts/freescale/imx93-var-dart-dt8mcustomboard.dts under kernel source directory and modify
&lpuart6 {
...
status = "okay";
};
to
&lpuart6 {
...
status = "disabled";
};
Other UARTs can be disabled in a similar manner by referencing the table above.
Configuring RS485 Half-Duplex
The i.MX93 supports controlling an rs485 transceiver driver enable using RTS_B. For more details, please refer to 63.3.4.4 Transceiver driver enable using RTS_B of the i.MX 93 Applications Processor Reference Manual.
RS485 is enabled in software by:
- Enabling the RTS pin in the device tree.
- Enabling RS485 in the serial driver.
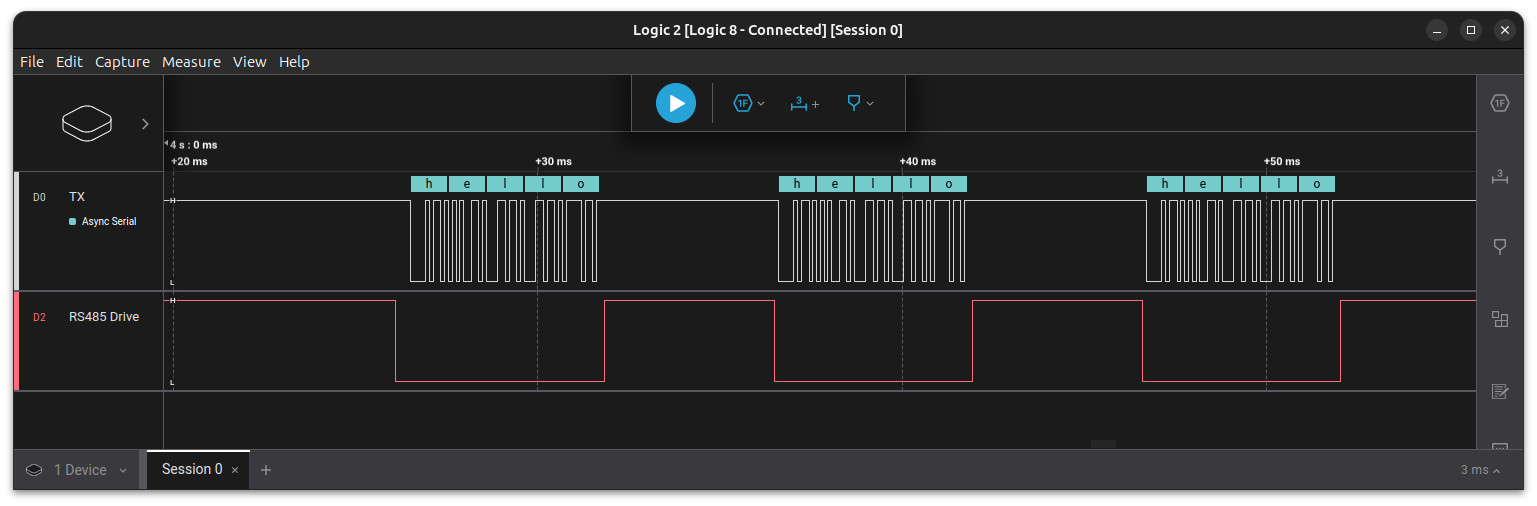
The example below demonstrates how to do this on the VAR-SOM-MX93 using /dev/ttyLP6 on J18.3 (TX), J18.4 (RX) and J17.8 (RTS).
First, disable the ov5640_mipi0 which uses the RTS pin:
&ov5640_mipi0 {
status = "disabled";
};
Then, configure the RTS pinmux in pinctrl_uart7:
pinctrl_uart7: uart7grp {
fsl,pins = <
...
MX93_PAD_GPIO_IO11__LPUART7_RTS_B 0x31e
...
>;
};
After booting the updated device tree, use the following python script to test RS485:
import sys
import serial
import serial.rs485
import time
def configure_rs485(port, data):
try:
# Open the serial port
ser = serial.Serial(port, baudrate=9600)
# Configure RS485
ser.rs485_mode = serial.rs485.RS485Settings(
delay_before_tx=0,
delay_before_rx=0,
rts_level_for_tx=False, # RTS is low during transmission
rts_level_for_rx=True, # RTS is high during reception
loopback=False
)
# Write data to the port three times with a delay of 10ms between each
for _ in range(3):
ser.write(data.encode())
time.sleep(0.01) # 10ms delay
# Close the serial port
ser.close()
print("Data sent successfully.")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error: {str(e)}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
if len(sys.argv) != 3:
print("Usage: python3 rs485.py <port> <data>")
else:
port = sys.argv[1]
data = sys.argv[2]
configure_rs485(port, data)
Finally, install pyserial and run the script:
root@imx93-var-som:~# pip3 install pyserial root@imx93-var-som:~# python3 rs485.py /dev/ttyLP6 "hello"
The following image was captured on a logic analyzer using this example: