Yocto Programming with VSCode
Visual Studio Code (VS Code) is a powerful, modern code editor that can be used to develop and debug C/C++ applications on Variscite System on Modules.
This guide demonstrates how to create and debug a C++ application using VS Code on the DART-MX8M-MINI.
Setup Host Computer Environment
Please follow the steps below to prepare a fresh Ubuntu 20.04 installation for VS Code debugging:
Install Dependencies
$ sudo apt-get -y update $ sudo apt-get -y install build-essential gdb gdb-multiarch git
Install VS Code
$ sudo snap install --classic code
Install VS Code Extensions
VS Code has a graphical interface for installing and managing extensions. To learn more, please see Using extensions in Visual Studio Code
For this guide, we will install the required extensions using the command line:
$ code --install-extension ms-vscode.cpptools
Install Yocto Toolchain
A toolchain is necessary for cross compiling applications. To install the toolchain, follow Variscite's Yocto Toolchain installation guide.
Create, cross compile, and run a new "Hello, World!" project
Open a new terminal, create an empty project directory and open VS Code:
$ mkdir ~/var-hello-world $ cd ~/var-hello-world $ code .
This will launch VS Code with ~/var-hello-world as working directory (which is currently empty):
Next, we will create the following files:
| main.cpp | Source code for the demo program hello.bin |
| Makefile | Makefile to cross compile main.cpp to hello.bin |
| .vscode/settings.json | VS Code file to configure global environment variables for the SDK/toolchain |
| .vscode/tasks.json | VS Code file to override or add new tasks. Runs Makefile when VS Code build command is executed.
|
| .vscode/c_cpp_properties.json | VS Code file to configure include path for IntelliSense. |
To create a new file or folder in VS Code, right click in the VS Code explorer view and select New File or New Folder:
Create a new file called main.cpp:
main.cpp:
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
printf("Hello, World!\n");
return 0;
}
Create a new Makefile to build hello.bin:
Makefile:
all: main.cpp $(CXX) $(CXXFLAGS) -Og main.cpp -g -o hello.bin clean: rm -f hello.bin
Create a new folder named .vscode. Then, create a new file .vscode/settings.json
.vscode/settings.json:
{
"VARISCITE": {
/* Target Device Settings */
"TARGET_IP":"192.168.0.141",
/* Project Settings */
"PROGRAM":"hello.bin",
/* Yocto SDK Configuration */
"ARCH":"aarch64-fslc-linux",
"OECORE_NATIVE_SYSROOT":"/opt/fslc-xwayland/3.1/sysroots/x86_64-fslcsdk-linux",
"SDKTARGETSYSROOT": "/opt/fslc-xwayland/3.1/sysroots/aarch64-fslc-linux",
/* Yocto SDK Constants */
"CC_PREFIX": "${config:VARISCITE.OECORE_NATIVE_SYSROOT}/usr/bin/${config:VARISCITE.ARCH}/${config:VARISCITE.ARCH}-",
"CXX": "${config:VARISCITE.CC_PREFIX}g++ --sysroot=${config:VARISCITE.SDKTARGETSYSROOT}",
"CC": "${config:VARISCITE.CC_PREFIX}gcc --sysroot=${config:VARISCITE.SDKTARGETSYSROOT}",
}
}
The table below describes the global variables in settings.json. They can be accessed in other json files, for example ${config:VARISCITE.TARGET_IP}:
| TARGET_IP | The IP Address of the DART-MX8M-MINI target device |
| PROGRAM | Must match the name of the binary generated by Makefile |
| ARCH | Architecture prefix for gcc, g++, gdb, etc. Align with CXX variable set by /opt/fslc-xwayland/3.1/environment-setup-aarch64-fslc-linux |
| OECORE_NATIVE_SYSROOT | Align with OECORE_NATIVE_SYSROOT variable set by /opt/fslc-xwayland/3.1/environment-setup-aarch64-fslc-linux |
| SDKTARGETSYSROOT | Align with SDKTARGETSYSROOT variable set by /opt/fslc-xwayland/3.1/environment-setup-aarch64-fslc-linux |
| CC_PREFIX | Full path to toolchain gcc, g++, etc binaries. |
| CXX | Path to cross g++ binary and sysroot |
| CC | Path to cross gcc binary and sysroot |
Create a new file .vscode/tasks.json. tasks.json has three root objects:
- options: Define CC and CXX environment variables for the Makefile.
- presentation: Configures the behavior of VS Code's integrated Terminal for all tasks.
- tasks: An array of task configurations. The example below creates a single 'build task that runs the Makefile when the VS Code build task is executed.
.vscode/tasks.json:
{
"version": "2.0.0",
/* Configure Yocto SDK Constants from settings.json */
"options": {
"env": {
"CXX": "${config:VARISCITE.CXX}", /* Used by Makefile */
"CC": "${config:VARISCITE.CC}", /* Used by Makefile */
}
},
/* Configure integrated VS Code Terminal */
"presentation": {
"echo": false,
"reveal": "always",
"focus": true,
"panel": "dedicated",
"showReuseMessage": true,
},
"tasks": [
/* Configure Build Task */
{
"label": "build",
"type": "shell",
"command": "make clean; make -j$(nproc)",
"problemMatcher": ["$gcc"]
},
]
}
Create vscode/c_cpp_properties.json to configure the include path for IntelliSense.
.vscode/c_cpp_properties.json:
{
"configurations": [
{
"name": "Linux",
"includePath": [
"${workspaceFolder}/**",
"${config:VARISCITE.SDKTARGETSYSROOT}/usr/include/**"
]
}
],
"version": 4
}
Your workspace should look similar to this:
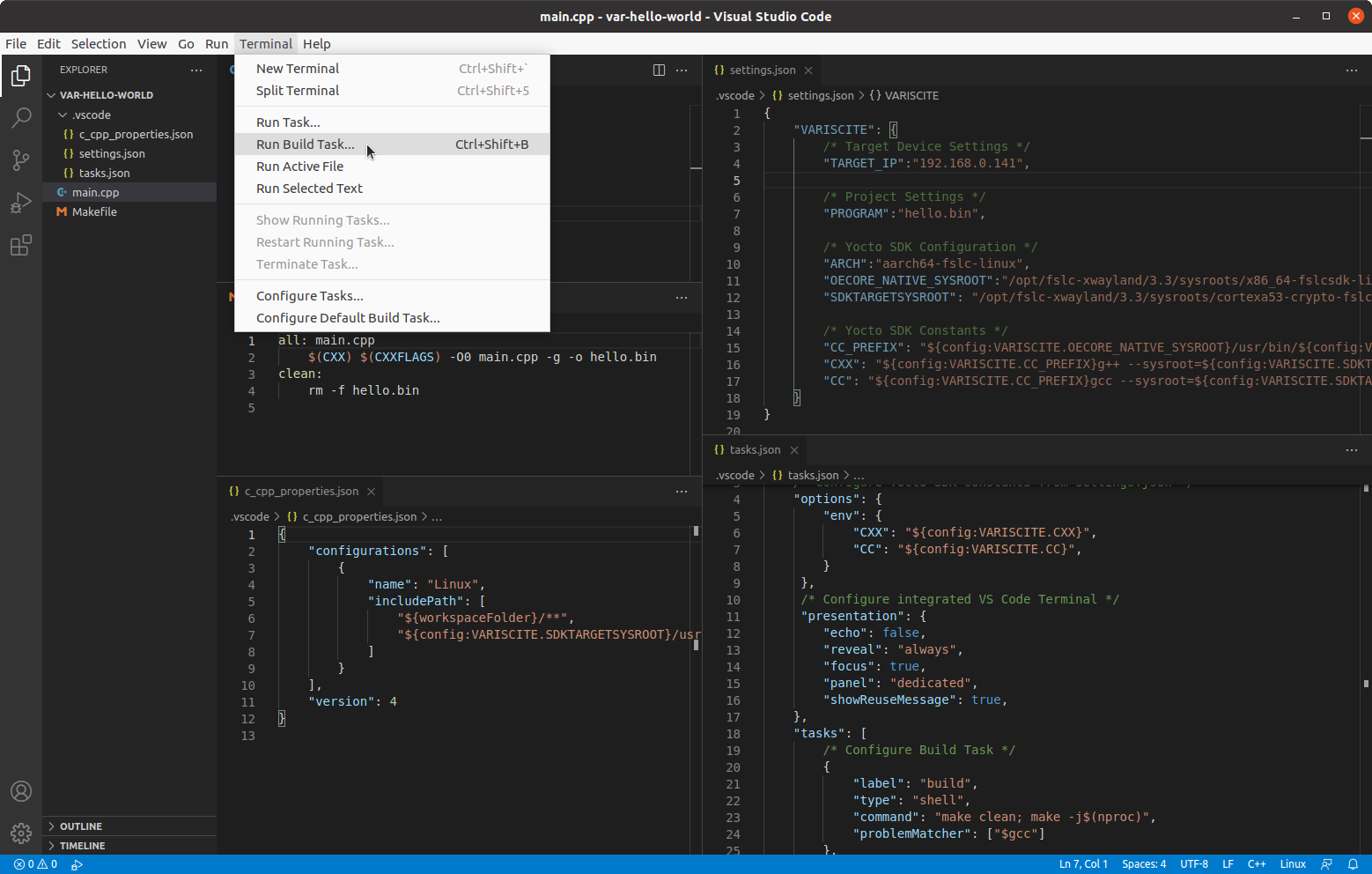
Cross compile the project by selecting Terminal->Run Build Task... or entering Ctrl+Shift+B and selecting Build:
Open a new VS Code terminal by selecting Terminal->New Terminal or entering Ctrl+Shift+`.
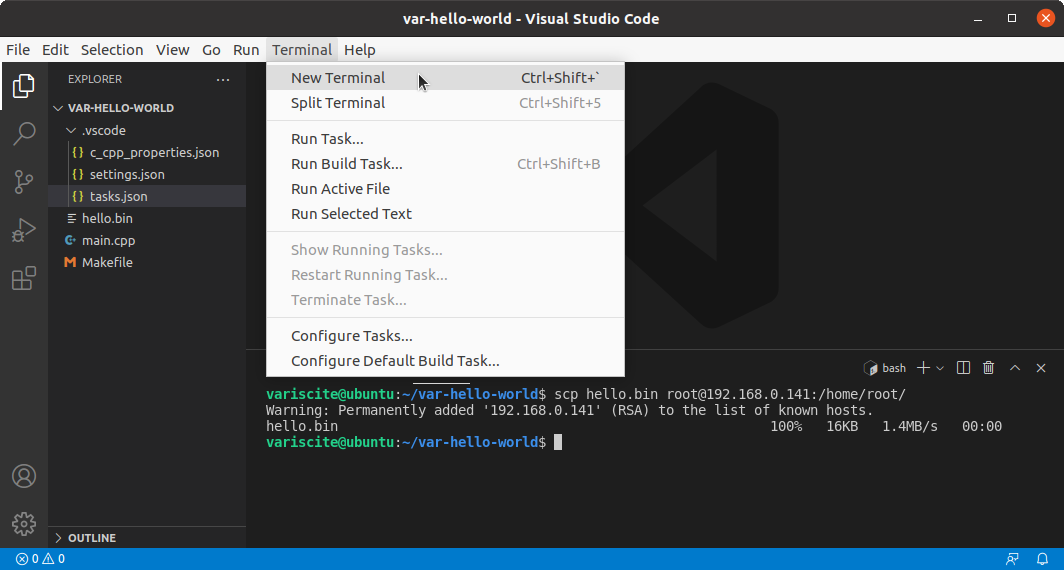
Deploy hello.bin to the target device using SCP:
$ scp hello.bin root@<ip addr>:/home/root/
Launch hello.bin on the target device:
# ./hello.bin Hello, World!
Remote Debugging with VS Code
After verifying hello.bin runs on the target device, we can now setup VS Code for remote debugging.
The working directory should currently have these files:
variscite@ubuntu:~/var-hello-world$ find .vscode/settings.json .vscode/tasks.json ./Makefile ./main.cpp ./hello.bin
To enable debugging, we will edit .vscode/tasks.json to add a var-deploy-gdb debug task and add two additional files to the project:
| var-deploy-gdb.sh | Generic script to deploy and launch gdbserver |
| .vscode/launch.json | VS Code file to configure debug settings. Runs var-build-and-debug in tasks.json
|
| .vscode/tasks.json | Edit to call var-deploy-gdb.sh prior to debugging.
|
Create var-deploy-gdb.sh
First, add a generic script deploy a program and launch gdbserver. The script requires two arguments:
TARGET_IP: The IP Address of the target devicePROGRAM: The name of the binary executable,hello.binin this example
In the end, tasks.json will run this script at the beginning of each debug session.
var-deploy-gdb.sh:
#!/bin/bash
readonly TARGET_IP="$1"
readonly PROGRAM="$2"
readonly TARGET_DIR="/home/root"
# Must match startsPattern in tasks.json
echo "Deploying to target"
# kill gdbserver on target and delete old binary
ssh root@${TARGET_IP} "sh -c '/usr/bin/killall -q gdbserver; rm -rf ${TARGET_DIR}/${PROGRAM} exit 0'"
# send the program to the target
scp ${PROGRAM} root@${TARGET_IP}:${TARGET_DIR}
# Must match endsPattern in tasks.json
echo "Starting GDB Server on Target"
# start gdbserver on target
ssh -t root@${TARGET_IP} "sh -c 'cd ${TARGET_DIR}; gdbserver localhost:3000 ${PROGRAM}'"
Create launch.json
VS Code has a powerful built in debugger capable of debugging many programming languages. In this step, we will add a configuration for debugging using the C/C++ extension:
.vscode/launch.json:
{
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [{
"name": "GDB debug",
"type": "cppdbg",
"request": "launch",
"program": "${config:VARISCITE.PROGRAM}",
"args": [],
"stopAtEntry": true,
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}",
"environment": [],
"console": "integratedTerminal",
"MIMode": "gdb",
"targetArchitecture": "arm64",
"preLaunchTask": "var-deploy-gdb",
"setupCommands": [{
"description": "Enable pretty-printing for gdb",
"text": "-enable-pretty-printing",
"ignoreFailures": true
}],
"miDebuggerPath": "/usr/bin/gdb-multiarch",
"miDebuggerServerAddress": "${config:VARISCITE.TARGET_IP}:3000",
}]
}
See the table below for important details regarding launch.json variables:
miDebuggerServerAddress |
Must match the IP Address of the target device |
program |
Must match the name of the binary generated by the the Makefile |
preLaunchTask |
Must match the name of the task in .vscode/tasks.json in the following step
|
Edit tasks.json
In launch.json, we created a preLaunchTask to run a task named var-deploy-gdb at the beginning of each debugging session. This task is configured by adding a new task var-deploy-gdb to .vscode/tasks.json:
.vscode/tasks.json:
{
"version": "2.0.0",
/* Configure Yocto SDK Constants from settings.json */
"options": {
"env": {
"CXX": "${config:VARISCITE.CXX}",
"CC": "${config:VARISCITE.CC}",
}
},
/* Configure integrated VS Code Terminal */
"presentation": {
"echo": false,
"reveal": "always",
"focus": true,
"panel": "dedicated",
"showReuseMessage": true,
},
"tasks": [
/* Configure launch.json (debug) preLaunchTask Task */
{
"label": "var-deploy-gdb",
"isBackground": true,
"problemMatcher":{
"base": "$gcc",
"background": {
"activeOnStart": true,
"beginsPattern": "Deploying to target",
"endsPattern": "Starting GDB Server on Target"
}
},
"type": "shell",
"command": "sh",
"args": [
"var-deploy-gdb.sh",
"${config:VARISCITE.TARGET_IP}",
"${config:VARISCITE.PROGRAM}"
],
"dependsOn": ["build"],
},
/* Configure Build Task */
{
"label": "build",
"type": "shell",
"command": "make clean; make -j$(nproc)",
"problemMatcher": ["$gcc"]
},
]
}
The following table summarizes the var-deploy-gdb configuration in tasks.json:
label |
Must match preLaunchTask in launch.json |
type |
This task will launch a shell |
command |
Launch sh, with arguments var-build-and-debug.sh 192.168.0.136 hello.bin
|
Launch a Debugging Session
After following the steps above, the working directory should now have these files:
~/var-hello-world$ find .vscode/c_cpp_properties.json .vscode/launch.json .vscode/settings.json .vscode/tasks.json ./Makefile ./var-deploy-gdb.sh ./main.cpp ./hello.bin
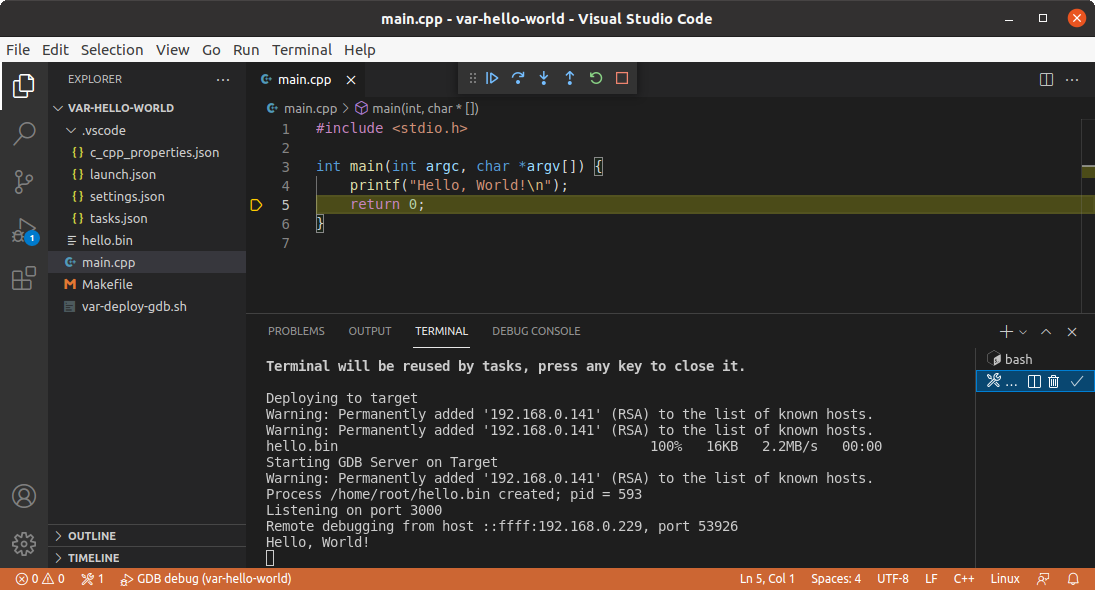
A new debugging session can be started by selecting Run->Start Debugging or by pressing 'F5' on the keyboard. VS Code will switch to the debug perspective and launch a gnome-terminal running gdbserver on the target device:
Example Project Source Code
The source code for this example is available from Variscite's Github repository:
$ git clone https://github.com/nsdrude-varigit/var-demos $ cd var-demos/hello-world
Launch VS Code:
$ code .
Configure the target device IP Address and SDK variables in .vscode/settings.json
Finally, start a debugging session by selecting Run->Start Debugging or pressing 'F5' on the keyboard.