Template:Yocto Create Bootable SD: Difference between revisions
| Line 100: | Line 100: | ||
Additionally, the file name of the recovery image output can be modified by setting something like the following in local.conf: | Additionally, the file name of the recovery image output can be modified by setting something like the following in local.conf: | ||
VAR_RECOVERY_SD_NAME = “my-recovery-image” | VAR_RECOVERY_SD_NAME = “my-recovery-image” | ||
Would produce a recovery image relative to the build folder of "./tmp/deploy/images/{{#var:MACHINE_NAME}}/my-recovery-image.{{#var:SDCARD_IMG_EXT}}" | Would produce a recovery image relative to the build folder of "./tmp/deploy/images/{{#var:MACHINE_NAME}}/my-recovery-image.{{#var:SDCARD_IMG_EXT}}"<br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
{{Note|'''Note:''' Please see the [{{#var:META_VARISCITE_SDK_GIT}}/blob/{{#var:META_VARISCITE_SDK_BRANCH}}/recipes-core/images/var-recovery-image.bb var-recovery-image recipe source] for advanced usages of the recovery image.}} | {{Note|'''Note:''' Please see the [{{#var:META_VARISCITE_SDK_GIT}}/blob/{{#var:META_VARISCITE_SDK_BRANCH}}/recipes-core/images/var-recovery-image.bb var-recovery-image recipe source] for advanced usages of the recovery image.}} | ||
Revision as of 19:45, 14 July 2023
Create a bootable SD card
SD card structure
This is the structure of our Recovery/Extended SD card:
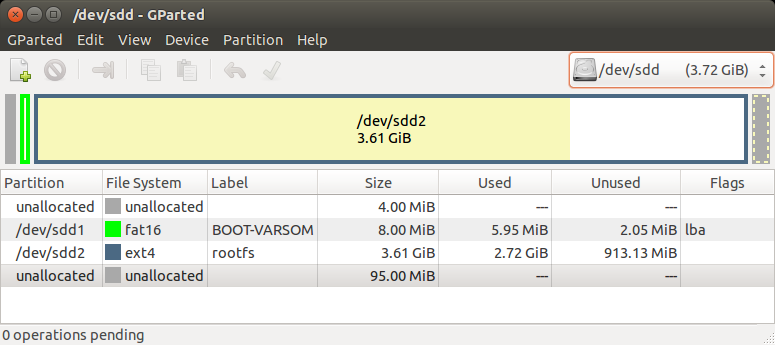
The SD card is divided into 3 sections as shown in the picture above:
- The first unallocated 4MiB are saved space for U-Boot. It can be replaced using the dd command as described in the Yocto Build U-Boot section.
- The first partition is a fat16 partition used for the device tree files and the kernel image file. You can copy them as described in the Yocto Build Linux section.
- The second partition is an ext4 partition that contains the complete root filesystem (including the kernel modules).
Note:
The last unallocated area is not used. It is there so that the rootfs will fit on any 4GB SD card, as not all 4GB SD cards are really the same size. If you want, you can use a program such as GParted to resize the roofs partition and make it end at the end of your specific SD card (of course, you can also use SD cards with much bigger capacity than 4GB, and then it makes more sense to resize the partition).
Also, if you create the extended SD card yourself by following the Create an extended SD card section below, and you use the '-a' option, the rootfs partition will end at the end of your specific SD card automatically.
Yocto pre-built bootable SD card
The Yocto build products contains many files as explained in the Build Results section. For example, fsl-image-gui-., depending on your build. This is a complete image to be flashed directly to an SD card.
Example usage:
$ sudo umount /dev/sdX*
# For GUI-X11 & Qt-X11 $ cd / Or # For Qt-FB $ cd / # For fsl-image-gui image (GUI-X11) $ sudo dd if=tmp/deploy/images//fsl-image-gui-. of=/dev/sdX bs=1M && sync Or # For fsl-image-qt image (Qt-X11 & Qt-FB) $ sudo dd if=tmp/deploy/images//fsl-image-qt-. of=/dev/sdX bs=1M && sync
Replace sdX with the right device name. This can be obtained by "dmesg" command on your host Linux PC, after the SD card reader is inserted.
- Note: Booting your system from an SD card requires pressing the boot-select button, or switching the relevant DIP switch to "Boot from SD card", according to the relevant start-up guide of your system
Yocto Recovery Image
Beginning in Yocto Langdale, Variscite has released a new recovery Yocto image recipe called “var-recovery-image.” This image is used to create a bootable SD card that contains another target image to be programmed to the eMMC. See the Yocto Recovery SD article on specifics of installing a recovery image.
Usage:
To create a recovery image, simply run the following from your Yocto environment:
$ bitbake var-recovery-image
This will produce an output relative to the build folder of "./tmp/deploy/images//var-recovery-image-." that can be flashed to the SD card. By default, this image boots fsl-image-gui and contains a fsl-image-gui target image to be programmed to eMMC.
You can also specify a different target eMMC image to be embedded in the recovery image by setting VAR_RECOVERY_TARGET_ROOTFS via the command line during build:
i.e.
$ VAR_RECOVERY_TARGET_ROOTFS="<desired-emmc-image-recipe>" bitbake var-recovery-image
Or alternatively, by setting this variable in local.conf:
VAR_RECOVERY_TARGET_ROOTFS = "<desired-emmc-image-recipe>"
Additionally, the file name of the recovery image output can be modified by setting something like the following in local.conf:
VAR_RECOVERY_SD_NAME = “my-recovery-image”
Would produce a recovery image relative to the build folder of "./tmp/deploy/images//my-recovery-image."
Create an extended SD card
Variscite provides the var-create-yocto-sdcard.sh script which creates our recovery SD card - an SD card based on the fsl-image-gui filesystem, which also contain the scripts and relevant binaries for installation to the internal storage of the SOM.
Later, you will be able to follow either the more automatic Yocto Recovery SD card guide or the more manual Installing Yocto to the SOM's internal storage guide.
Note:
This is essentially the same as our pre-built Recovery SD image, with the following main differences:
- The pre-built image's rootfs partition size is 3700MiB, which is also the default size when using the script, but the script also has an option to set the rootfs partition size to fill the whole free space of the used SD card. Anyway, you can always resize the partition later with an external tool such as gparted.
Naturally, the pre-built image is more straight forward and easier to use, while the script method is easier to customize.
Usage:
- Follow the Setup and build Yocto guide, and bitbake fsl-image-gui.
- Plug-in the SD card to your Linux Host PC, run dmesg and see which device is added (i.e. /dev/sdX or /dev/mmcblkX)
$ cd $ sudo MACHINE= sources//scripts/var_mk_yocto_sdcard/var-create-yocto-sdcard.sh <options> /dev/sdX (Replace /dev/sdX with your actual device)
options: -h Display help message -s Only show partition sizes to be written, without actually write them -a Automatically set the rootfs partition size to fill the SD card -r Select alternative rootfs for recovery images (default: /tmp/deploy/images//fsl-image-gui-.*)
If you don't use the '-a' option, a default rootfs size of 3700MiB will be used The '-r' option allows you to create a bootable SD card with an alternative image for the installation to NAND flash or eMMC. Example: "-r tmp/deploy/images//fsl-image-qt-" -- selected the "Qt image with X11" recovery image
Create an extended SD card image using a loop device
It is also possible to use the var-create-yocto-sdcard.sh script to create an extended SD card image, while using a loop device instead of attaching a real SD card.
Create an empty file using the following command:
$ dd if=/dev/zero of=-extended-sd.img bs=1M count=7420
The above command creates a 7420MiB file representing the SD card.
Attach the first available loop device to this file:
$ sudo losetup -Pf -extended-sd.img
To find the actual loop device being used, run:
$ losetup -a | grep -extended-sd.img
Write the content to the loop device to generate the SD card image:
$ sudo MACHINE= sources//scripts/var_mk_yocto_sdcard/var-create-yocto-sdcard.sh <options> /dev/loopX
(Replace /dev/loopX with your actual loop device, e.g. /dev/loop0)
Detach the loop device from the file:
$ sudo losetup -d /dev/loopX
To compress the SD card image file use the following command:
$ gzip -9 -extended-sd.img
To write the SD card image to a real SD card device use the following command:
$ zcat -extended-sd.img.gz | sudo dd of=/dev/sdX bs=1M && sync
(Replace /dev/sdX with your actual SD device, e.g. /dev/sdb)