B2QT Build Release: Difference between revisions
| (67 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<!-- Set release according to "release" parameter in URL and use RELEASE_MORTY_V1.0_VAR-SOM-MX6 as default | <!-- Set release according to "release" parameter in URL and use RELEASE_MORTY_V1.0_VAR-SOM-MX6 as default | ||
--> {{ | --> {{INIT_RELEASE_PARAM|RELEASE_MORTY_B2QT_V1.0_VAR-SOM-MX6}}<!-- | ||
--> {{#lst:B2QT_Platform_Customization|{{#var:RELEASE_PARAM | --> {{#lst:B2QT_Platform_Customization|{{#var:RELEASE_PARAM}}}} <!-- | ||
--> {{PageHeader|{{#var:HARDWARE_NAME}} - Boot to Qt {{#var:B2QT_BSP_VERSION}} based on Yocto {{#var:YOCTO_NAME}} {{DocImage|category1=Boot2Qt|category2={{#var:HARDWARE_NAME}}}} }}__toc__ | --> {{PageHeader|{{#var:HARDWARE_NAME}} - Boot to Qt {{#var:B2QT_BSP_VERSION}} based on Yocto {{#var:YOCTO_NAME}} {{DocImage|category1=Boot2Qt|category2={{#var:HARDWARE_NAME}}}} }}__toc__ | ||
<!-- Set local variables | |||
--> {{COMMON_YOCTO_VARS}} <!-- Include common yocto variables | |||
--> {{#vardefine:LOC_B2QT_IMAGE_NAME | {{#varexists: DEFAULT_IMAGE_BB_NAME | {{#var:DEFAULT_IMAGE_BB_NAME}} | b2qt-embedded-qt5-image }} }} <!-- | |||
--> {{#vardefine:LOC_B2QT_TOOLCHAIN_NAME | {{#varexists: DEFAULT_TOOLCHAIN_BB_NAME | {{#var:DEFAULT_TOOLCHAIN_BB_NAME}} | meta-toolchain-b2qt-embedded-qt5-sdk }} }} <!-- | |||
-->{{#vardefine:UBUNTU_COMPAT|16.04}}<!-- | |||
-->{{#vardefine:UBUNTU_COMPAT|{{#ifeq:{{#var:YOCTO_NAME}}|Morty|14.04/16.04|{{#var:UBUNTU_COMPAT}}}}}}<!-- | |||
-->{{#vardefine:UBUNTU_COMPAT|{{#ifeq:{{#var:YOCTO_NAME}}|Zeus|18.04|{{#var:UBUNTU_COMPAT}}}}}}<!-- | |||
-->{{#vardefine:UBUNTU_COMPAT|{{#ifexpr: {{#var:YOCTO_VERSION}} >= 3.1|18.04/20.04|{{#var:UBUNTU_COMPAT}}}}}}<!-- | |||
-->{{#vardefine:UBUNTU_COMPAT|{{#ifexpr: {{#var:YOCTO_VERSION}} >= 4.0|18.04/20.04/22.04|{{#var:UBUNTU_COMPAT}}}}}} <!-- | |||
-->{{#vardefine:REPO_VERSION|repo}}<!-- | |||
-->{{#vardefine:REPO_VERSION|{{#ifeq:{{#var:YOCTO_NAME}}|Morty|repo-1|{{#var:REPO_VERSION}}}}}}<!-- | |||
-->{{#vardefine:REPO_VERSION|{{#ifeq:{{#var:YOCTO_NAME}}|Zeus|repo-1|{{#var:REPO_VERSION}}}}}} | |||
= About Boot to Qt = | = About Boot to Qt = | ||
| Line 17: | Line 30: | ||
= Requirements = | = Requirements = | ||
Please make sure your host PC is running Ubuntu {{#var:UBUNTU_COMPAT}} 64-bit and is up to date: | |||
$ sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get dist-upgrade | |||
Then, install the following packages: | |||
$ sudo apt-get install gawk wget git git-lfs diffstat unzip texinfo gcc-multilib \ | |||
build-essential chrpath socat cpio python python3 python3-pip python3-pexpect \ | |||
xz-utils debianutils iputils-ping libsdl1.2-dev xterm libyaml-dev libssl-dev | |||
$ sudo apt-get install autoconf libtool libglib2.0-dev libarchive-dev \ | |||
sed cvs subversion coreutils texi2html docbook-utils python-pysqlite2 \ | |||
help2man make gcc g++ g++-multilib desktop-file-utils libgl1-mesa-dev libglu1-mesa-dev \ | |||
mercurial automake groff curl lzop asciidoc u-boot-tools dos2unix mtd-utils pv \ | |||
libncurses5 libncurses5-dev libncursesw5-dev libelf-dev zlib1g-dev bc rename \ | |||
zstd libgnutls28-dev | |||
{{#ifexpr: {{#var:YOCTO_VERSION}} >= 3.1| | |||
$ sudo apt-get install python3-git zstd liblz4-tool | |||
| | |||
$ sudo apt-get install python-git | |||
}} | |||
{{#ifexpr:{{#rpos:{{#var:UBUNTU_COMPAT}}|16.04}} >= 0|{{Ubuntu16_Python}}|}}<!-- | |||
-->{{#ifexpr:{{#rpos:{{#var:UBUNTU_COMPAT}}|22.04}} >= 0|{{Ubuntu22_Python}}|}} | |||
Next, configure git: | |||
$ git config --global user.name "Your Name" | |||
$ git config --global user.email "Your Email" | |||
And finally, install the repo tool: | |||
$ mkdir -p ~/bin | |||
$ curl https://commondatastorage.googleapis.com/git-repo-downloads/{{#var:REPO_VERSION}} > ~/bin/repo | |||
$ chmod a+x ~/bin/repo | |||
$ export PATH=~/bin:$PATH | |||
{{Note|'''Note:''' Variscite provides Docker containers that can be used for a development environment as an alternative to using a virtual machine or a dedicated computer. | |||
To learn more, please see Variscite's [[Docker_Build_Environment | Docker Build Environment]] guide.}} | |||
= Setting Up Yocto Build Environment = | = Setting Up Yocto Build Environment = | ||
{{#if: {{#var:MACHINE_NAME_B0}} | | |||
{{note| The instructions in the following sections, apply for machine '''{{#var:MACHINE_NAME}}'''. If you have '''{{#var:MACHINE_DESC_B0}}''' remind to use machine '''{{#var:MACHINE_NAME_B0}}'''.}} | |||
| }} | |||
Run the setup script that initializes the Yocto environment. | Run the setup script that initializes the Yocto environment. | ||
$ mkdir ~/var-b2qt | $ mkdir -p ~/var-b2qt/sources/ | ||
$ cd ~/var-b2qt | $ cd ~/var-b2qt/sources/ | ||
$ git clone {{#var:B2QT_GIT}} -b {{#var:B2QT_BRANCH}} | $ git clone {{#var:B2QT_GIT}} -b {{#var:B2QT_BRANCH}} | ||
$ cd meta-variscite-boot2qt | $ cd .. | ||
$ ./sources/meta-variscite-boot2qt/b2qt-init-build-env init --device {{#var:MACHINE_NAME}} | |||
b2qt-init-build-env has the following additional command line options: | b2qt-init-build-env has the following additional command line options: | ||
| Line 42: | Line 90: | ||
For all command line options, see: | For all command line options, see: | ||
$ ./b2qt-init-build-env help | $ ./sources/meta-variscite-boot2qt/b2qt-init-build-env help | ||
= Building the Image and Toolchain = | = Building the Image and Toolchain = | ||
| Line 52: | Line 100: | ||
Yocto recipes for Boot to Qt for embedded Linux have two main targets to build: The target image, and the external toolchain that can be used with Qt Creator for building Qt applications. | Yocto recipes for Boot to Qt for embedded Linux have two main targets to build: The target image, and the external toolchain that can be used with Qt Creator for building Qt applications. | ||
$ MACHINE={{#var:MACHINE_NAME}} bitbake | $ MACHINE={{#var:MACHINE_NAME}} bitbake {{#var:LOC_B2QT_IMAGE_NAME}} | ||
$ MACHINE={{#var:MACHINE_NAME}} bitbake | $ MACHINE={{#var:MACHINE_NAME}} bitbake {{#var:LOC_B2QT_TOOLCHAIN_NAME}} | ||
The target rootfs image is located at: | The target rootfs image is located at: | ||
~/var-b2qt | ~/var-b2qt/build-{{#var:MACHINE_NAME}}/tmp/deploy/images/{{#var:MACHINE_NAME}}/{{#var:LOC_B2QT_IMAGE_NAME}}-{{#var:MACHINE_NAME}}.wic.gz | ||
and the new toolchain installation file is: | and the new toolchain installation file is: | ||
~/var-b2qt | ~/var-b2qt/build-{{#var:MACHINE_NAME}}/tmp/deploy/sdk/b2qt-x86_64-{{#var:LOC_B2QT_TOOLCHAIN_NAME}}-{{#var:MACHINE_NAME}}.sh | ||
{{#varexists: YOCTO_BUILD_RESULTS_SECTION | | |||
== Build Results == | |||
The resulting images are located in tmp/deploy/images/{{#var:MACHINE_NAME}}. | |||
{{#lst:Yocto_Platform_Customization|{{#var:YOCTO_BUILD_RESULTS_SECTION}}}} | |||
|}} | |||
= Create a bootable SD card = | |||
== SD card structure == | |||
{{#ifeq: {{#var:SOC_SERIES}} | imx8 | | |||
This is the structure of our Recovery/Extended SD card:<br> | |||
[[File:SD_card_part_mx8m.png]]<br><br> | |||
The SD card is divided into 2 sections as shown in the picture above:<br> | |||
* The first unallocated 8MiB section reserved for U-Boot. It can be replaced using the dd command{{#varexists:TOOLCHAIN_LOCATION| as described in the {{Varlink2|Yocto Build U-Boot|{{#var:RELEASE_LINK}}}} section|}}.<br> | |||
* The first partition is an ext4 partition that contains the complete root filesystem (including kernel image and device tree files under /boot).<br><br> | |||
| | |||
This is the structure of our Recovery/Extended SD card:<br> | |||
[[File:SD_card_part_v50.png]]<br><br> | |||
The SD card is divided into 3 sections as shown in the picture above:<br> | |||
* The first unallocated 4MiB are saved space for U-Boot. It can be replaced using the dd command{{#varexists:TOOLCHAIN_LOCATION| as described in the {{Varlink2|Yocto Build U-Boot|{{#var:RELEASE_LINK}}}} section|}}.<br> | |||
* The first partition is a fat16 partition used for the device tree files and the kernel image file.{{#varexists:TOOLCHAIN_LOCATION| You can copy them as described in the {{Varlink2|Yocto Build Linux|{{#var:RELEASE_LINK}}}} section.|}}<br> | |||
* The second partition is an ext4 partition that contains the complete root filesystem (including the kernel modules).<br><br> | |||
}} | |||
Note:<br> | |||
The last unallocated area is not used. It is there so that the rootfs will fit on any 4GB SD card, as not all 4GB SD cards are really the same size. If you want, you can use a program such as GParted to resize the roofs partition and make it end at the end of your specific SD card (of course, you can also use SD cards with much bigger capacity than 4GB, and then it makes more sense to resize the partition).<br> | |||
Also, if you create the extended SD card yourself by following the [[#Create_an_extended_SD_card | Create an extended SD card]] section below, and you use the '-a' option, the rootfs partition will end at the end of your specific SD card automatically.<br> | |||
= | ==B2Qt pre-built bootable SD card== | ||
The B2Qt build products contains a complete image to be flashed directly to an SD card.<br> | |||
Example usage: | |||
$ sudo umount /dev/sdX* | $ sudo umount /dev/sdX* | ||
$ zcat tmp/deploy/images/{{#var:MACHINE_NAME}}/{{#var:LOC_B2QT_IMAGE_NAME}}-{{#var:MACHINE_NAME}}.{{#var:SDCARD_IMG_EXT}} <nowiki>|</nowiki> sudo dd of=/dev/sdX bs=1M && sync | |||
Replace sdX with the right device name. This can be obtained by "dmesg" command on your host Linux PC, after the SD card reader is inserted. | |||
* <span style="color:red">Note:</span> Booting your system from an SD card requires pressing the boot-select button, or switching the relevant DIP switch to "Boot from SD card", according to the relevant start-up guide of your system<br><br> | |||
Drawbacks of the native .{{#var:SDCARD_IMG_EXT}} b2qt-built image, (relative to the Recovery/Extended SD card): | |||
* The rootfs partition doesn't use the entire SD card. | |||
* The rootfs partition is not labeled as rootfs. | |||
* The NAND flash and eMMC installation scripts and images are not included. | |||
= | == Create an extended SD card == | ||
Variscite provides the var-create-yocto-sdcard.sh script which creates our NAND/eMMC recovery SD card. The script copies the NAND/eMMC flash burning scripts and relevant binaries for your convenience.<br> | Variscite provides the var-create-yocto-sdcard.sh script which creates our NAND/eMMC recovery SD card. The script copies the NAND/eMMC flash burning scripts and relevant binaries for your convenience.<br> | ||
Later, you will be able to follow {{Varlink2| | Later, you will be able to follow {{Varlink2|Boot2QT Recovery SD card|{{#var:RELEASE_LINK}}}} guide to burn your images to NAND flash or eMMC.<br><br> | ||
Note:<br> | |||
This is essentially the same as our pre-built Recovery SD image, with the following main differences:<br> | |||
{{#ifeq: {{#var:HARDWARE_NAME}} | VAR-SOM-MX6 | | |||
* The Android recovery (Android-eMMC) is only present on the pre-built SD image, and not on the SD card built from the Yocto script.<br> | |||
}} | |||
* The pre-built image's rootfs partition size is 3700MiB, which is also the default size when using the script, but the script also has an option to set the rootfs partition size to fill the whole free space of the used SD card. Anyway, you can always resize the partition later with an external tool such as gparted.<br> | |||
Naturally, the pre-built image is more straight forward and easier to use, while the script method is easier to customize.<br><br> | |||
Plug the SD card | Usage:<br> | ||
* Follow the [[#Setup and build Yocto|Setup and build Yocto]] guide, and bitbake {{#var:LOC_B2QT_IMAGE_NAME}}. | |||
* Plug-in the SD card to your Linux HOST PC, run dmesg and see which device is added (i.e. /dev/sdX or /dev/mmcblkX) | |||
$ cd ~/var-b2qt | $ cd ~/var-b2qt | ||
$ sudo MACHINE={{#var:MACHINE_NAME}} sources/ | $ sudo MACHINE={{#var:MACHINE_NAME}} sources/{{#var:META_VARISCITE_SDK}}/scripts/var_mk_yocto_sdcard/var-create-yocto-sdcard.sh /dev/sdX | ||
Replace /dev/sdX with your actual device name, e.g. /dev/sdb | Replace /dev/sdX with your actual device name, e.g. /dev/sdb | ||
=== Create an extended SD card image using a loop device === | |||
It is also possible to use the var-create-yocto-sdcard.sh script to create an extended SD card image, while using a loop device instead of attaching a real SD card.<br> | |||
<br> | |||
$ cd ~/var-b2qt | |||
Create an empty file using the following command: | |||
$ dd if=/dev/zero of={{#var:MACHINE_NAME}}-extended-sd.img bs=1M count=3720 | |||
The above command creates a 3720MiB file representing the SD card.<br> | |||
<br> | |||
Attach the first available loop device to this file: | |||
$ sudo losetup -Pf {{#var:MACHINE_NAME}}-extended-sd.img | |||
To find the actual loop device being used, run: | |||
$ losetup -a | grep {{#var:MACHINE_NAME}}-extended-sd.img | |||
Write the content to the loop device to generate the SD card image: | |||
$ sudo MACHINE={{#var:MACHINE_NAME}} sources/{{#var:META_VARISCITE_SDK}}/scripts/var_mk_yocto_sdcard/var-create-yocto-sdcard.sh <options> /dev/loopX | |||
(Replace /dev/loopX with your actual loop device, e.g. /dev/loop0)<br> | |||
<br> | |||
Detach the loop device from the file: | |||
$ sudo losetup -d /dev/loopX | |||
To compress the SD card image file use the following command: | |||
$ gzip -9 {{#var:MACHINE_NAME}}-extended-sd.img | |||
To write the SD card image to a real SD card device use the following command: | |||
$ zcat {{#var:MACHINE_NAME}}-extended-sd.img.gz | sudo dd of=/dev/sdX bs=1M && sync | |||
(Replace /dev/sdX with your actual SD device, e.g. /dev/sdb) | |||
= Boot the board with a bootable SD card = | |||
{{#ifeq: {{#var:HARDWARE_NAME}} | DART-6UL | | |||
Note: <span style="color:red">The WiFi is not operational when booting from SD card</span>, as the WiFi and SD card are using the same SDIO interface.<br> | |||
A typical use-case is to boot from an SD card, flash the eMMC/NAND flash, and re-boot from the eMMC/NAND flash to have the WiFi operational. | |||
|}} | |||
{{#ifeq: {{#var:HARDWARE_NAME}} | DART-MX8M | | |||
Note: <span style="color:red">The WiFi is not operational when booting from SD card</span>, as the WiFi and SD card are using the same SDIO interface.<br> | |||
A typical use-case is to boot from an SD card, flash the eMMC, and re-boot from the eMMC to have the WiFi operational. | |||
|}} | |||
{{#varexists: YOCTO_BOOT_BOARD_SECTION | | |||
== Setting the Boot Mode == | |||
{{#lst:Yocto_Platform_Customization|{{#var:YOCTO_BOOT_BOARD_SECTION}}}} | |||
|}} | |||
{{#ifeq: {{#var:SOC_SERIES}} | imx8 | | |||
| | |||
== Automatic device tree selection in U-Boot == | |||
As shown in the [[#Build_Results| Build Results]] table above, we have different kernel device trees, corresponding to our different H/W configurations.<br> | |||
We implemented a script in U-Boot's environment, which sets the fdt_file environment variable based on the detected hardware. | |||
=== Enable/Disable automatic device tree selection === | |||
To enable the automatic device tree selection in U-Boot (already enabled by default): | |||
<pre> | |||
$ setenv fdt_file undefined | |||
$ saveenv | |||
</pre> | |||
To disable the automatic device tree selection in U-Boot, set the device tree file manually: | |||
<pre> | |||
$ setenv fdt_file YOUR_DTB_FILE | |||
$ saveenv | |||
</pre> | |||
Useful example: To list all files in the boot partition (where the dtb files are by default) of an SD card: | |||
<pre> | |||
$ ls mmc 0:1 | |||
</pre> | |||
<!-- Make NOTE for DART-6UL only --> | |||
{{#ifeq: {{#var:HARDWARE_NAME}} | DART-6UL | | |||
{{note|Comment:<br>Make sure you don't set an inappropriate dtb file, like a dtb with nand on a SOM that has eMMC, or a dtb for mx6ull on a SOM with an mx6ul SOC.|info}} | |||
|}} | |||
}} | |||
Latest revision as of 20:02, 1 November 2023
This page is using the default release RELEASE_MORTY_B2QT_V1.0_VAR-SOM-MX6.
To view this page for a specific Variscite SoM and software release, please follow these steps:
- Visit variwiki.com
- Select your SoM
- Select the software release
About Boot to Qt
Boot to Qt is a light-weight, Qt-optimized, full software stack for embedded Linux systems that is installed into the actual target device.
The stack can be customized to production with Build-Your-Own-Stack tooling, including proprietary Yocto Project recipes.
The full B2Qt documentation is available at Qt for Device Creation official page.
Requirements
Please make sure your host PC is running Ubuntu 14.04/16.04 64-bit and is up to date:
$ sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get dist-upgrade
Then, install the following packages:
$ sudo apt-get install gawk wget git git-lfs diffstat unzip texinfo gcc-multilib \ build-essential chrpath socat cpio python python3 python3-pip python3-pexpect \ xz-utils debianutils iputils-ping libsdl1.2-dev xterm libyaml-dev libssl-dev $ sudo apt-get install autoconf libtool libglib2.0-dev libarchive-dev \ sed cvs subversion coreutils texi2html docbook-utils python-pysqlite2 \ help2man make gcc g++ g++-multilib desktop-file-utils libgl1-mesa-dev libglu1-mesa-dev \ mercurial automake groff curl lzop asciidoc u-boot-tools dos2unix mtd-utils pv \ libncurses5 libncurses5-dev libncursesw5-dev libelf-dev zlib1g-dev bc rename \ zstd libgnutls28-dev $ sudo apt-get install python-git
For Ubuntu 14.04 and 16.04, the repo tool requires you to upgrade to Python 3.6:
sudo apt-get install build-essential checkinstall libreadline-gplv2-dev libncursesw5-dev libssl-dev \
libsqlite3-dev tk-dev libgdbm-dev libc6-dev libbz2-dev && \
wget https://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.6.9/Python-3.6.9.tar.xz && \
tar xvf Python-3.6.9.tar.xz && \
cd Python-3.6.9/ && \
./configure && \
sudo make altinstall -j 16
Next, configure git:
$ git config --global user.name "Your Name" $ git config --global user.email "Your Email"
And finally, install the repo tool:
$ mkdir -p ~/bin $ curl https://commondatastorage.googleapis.com/git-repo-downloads/repo-1 > ~/bin/repo $ chmod a+x ~/bin/repo $ export PATH=~/bin:$PATH
Setting Up Yocto Build Environment
Run the setup script that initializes the Yocto environment.
$ mkdir -p ~/var-b2qt/sources/ $ cd ~/var-b2qt/sources/ $ git clone https://github.com/varigit/meta-variscite-boot2qt.git -b morty-var01 $ cd .. $ ./sources/meta-variscite-boot2qt/b2qt-init-build-env init --device var-som-mx6
b2qt-init-build-env has the following additional command line options:
- list-devices: show all supported devices that can be used for a Boot to Qt build
- mirror: create a local mirror of the yocto repositories. This enables you to use the same repository downloads for multiple build environments, when initializing with init --reference <mirror path>.
For all command line options, see:
$ ./sources/meta-variscite-boot2qt/b2qt-init-build-env help
Building the Image and Toolchain
After the Yocto environment is set up, you need to configure the build environment for your target device:
$ MACHINE=var-som-mx6 source ./setup-environment.sh
Yocto recipes for Boot to Qt for embedded Linux have two main targets to build: The target image, and the external toolchain that can be used with Qt Creator for building Qt applications.
$ MACHINE=var-som-mx6 bitbake b2qt-embedded-qt5-image $ MACHINE=var-som-mx6 bitbake meta-toolchain-b2qt-embedded-qt5-sdk
The target rootfs image is located at:
~/var-b2qt/build-var-som-mx6/tmp/deploy/images/var-som-mx6/b2qt-embedded-qt5-image-var-som-mx6.wic.gz
and the new toolchain installation file is:
~/var-b2qt/build-var-som-mx6/tmp/deploy/sdk/b2qt-x86_64-meta-toolchain-b2qt-embedded-qt5-sdk-var-som-mx6.sh
Build Results
The resulting images are located in tmp/deploy/images/var-som-mx6.
| Image Name |
Description |
|---|---|
| b2qt-embedded-qt5-image-var-som-mx6. | This image is for SD card boot. It can be flashed as-is on an SD card that can then be used to boot your system, according to the relevant startup-guide of your product (usually requires to press the boot select button, or toggle a DIP switch). For detailed information refer to the Create a bootable SD card section below. |
| b2qt-embedded-qt5-image-var-som-mx6.tar.gz | Tarball with rootfs files. Can be used to create an NFS root file system on the host. See the Yocto Setup TFTP/NFS section for more info. Also used to create our extended SD card. See the Create a bootable SD card section below. |
| b2qt-embedded-qt5-image-var-som-mx6_128kbpeb.ubi | A complete UBI image containing a UBIFS volume, for writing to NAND flash with 128KiB PEB. |
| b2qt-embedded-qt5-image-var-som-mx6_256kbpeb.ubi | A complete UBI image containing a UBIFS volume, for writing to NAND flash with 256KiB PEB. |
| uImage | Linux kernel image, same binary for SD card/eMMC or NAND flash. |
| SPL-sd | SPL built for SD card boot or eMMC boot. |
| SPL-nand | SPL built for NAND flash. |
| u-boot.img-sd | U-Boot built for SD card boot or eMMC boot. |
| u-boot.img-nand | U-Boot built for NAND flash. |
| Device Tree Name |
SOM type |
Carrier Board type |
LCD Type |
Evaluation Kit name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| uImage-imx6q-var-som-cap.dtb | VAR-SOM-MX6_V2 (Quad / Dual) | VAR-MX6CustomBoard | Capacitive touch | VAR-DVK-MX6_V2-PRO VAR-STK-MX6_V2 |
| uImage-imx6q-var-som-res.dtb | VAR-SOM-MX6_V2 (Quad / Dual) | VAR-MX6CustomBoard | Resistive touch | VAR-DVK-MX6_V2-PRO VAR-STK-MX6_V2 |
| uImage-imx6q-var-som-vsc.dtb | VAR-SOM-MX6_V2 (Quad / Dual) | VAR-SOLOCustomBoard | Capacitive LVDS touch | N/A |
| uImage-imx6dl-var-som-cap.dtb | VAR-SOM-MX6_V2 (DualLite / Solo) | VAR-MX6CustomBoard | Capacitive touch | N/A |
| uImage-imx6dl-var-som-res.dtb | VAR-SOM-MX6_V2 (DualLite / Solo) | VAR-MX6CustomBoard | Resistive touch | N/A |
| uImage-imx6dl-var-som-vsc.dtb | VAR-SOM-MX6_V2 (DualLite / Solo) | VAR-SOLOCustomBoard | Capacitive LVDS touch | N/A |
| uImage-imx6qp-var-som-cap.dtb | VAR-SOM-MX6_V2 (QuadPlus / DualPlus) | VAR-MX6CustomBoard | Capacitive touch | N/A |
| uImage-imx6qp-var-som-res.dtb | VAR-SOM-MX6_V2 (QuadPlus / DualPlus) | VAR-MX6CustomBoard | Resistive touch | N/A |
| uImage-imx6qp-var-som-vsc.dtb | VAR-SOM-MX6_V2 (QuadPlus / DualPlus) | VAR-SOLOCustomBoard | Capacitive LVDS touch | N/A |
| uImage-imx6dl-var-som-solo-cap.dtb | VAR-SOM-SOLO / VAR-SOM-DUAL | VAR-MX6CustomBoard | Capacitive touch | N/A |
| uImage-imx6dl-var-som-solo-res.dtb | VAR-SOM-SOLO / VAR-SOM-DUAL | VAR-MX6CustomBoard | Resistive touch | N/A |
| uImage-imx6dl-var-som-solo-vsc.dtb | VAR-SOM-SOLO / VAR-SOM-DUAL | VAR-SOLOCustomBoard | Capacitive LVDS touch | VAR-DVK-SOLO/DUAL VAR-STK-SOLO/DUAL |
| uImage-imx6q-var-dart.dtb | DART-MX6 | VAR-DT6CustomBoard | Capacitive LVDS touch | VAR-DVK-DT6 VAR-STK-DT6 |
Create a bootable SD card
SD card structure
This is the structure of our Recovery/Extended SD card:
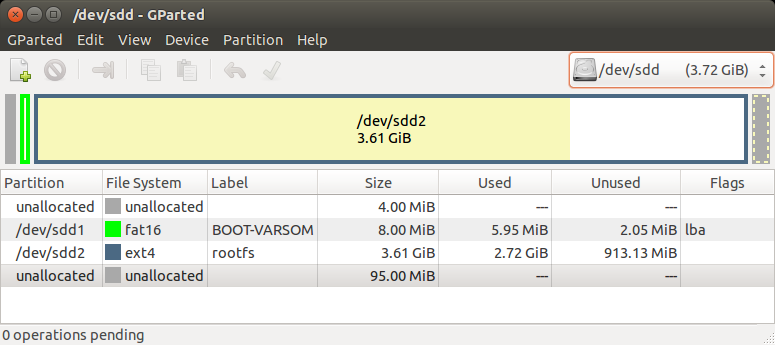
The SD card is divided into 3 sections as shown in the picture above:
- The first unallocated 4MiB are saved space for U-Boot. It can be replaced using the dd commandas described in the Yocto Build U-Boot section.
- The first partition is a fat16 partition used for the device tree files and the kernel image file.You can copy them as described in the Yocto Build Linux section.
- The second partition is an ext4 partition that contains the complete root filesystem (including the kernel modules).
Note:
The last unallocated area is not used. It is there so that the rootfs will fit on any 4GB SD card, as not all 4GB SD cards are really the same size. If you want, you can use a program such as GParted to resize the roofs partition and make it end at the end of your specific SD card (of course, you can also use SD cards with much bigger capacity than 4GB, and then it makes more sense to resize the partition).
Also, if you create the extended SD card yourself by following the Create an extended SD card section below, and you use the '-a' option, the rootfs partition will end at the end of your specific SD card automatically.
B2Qt pre-built bootable SD card
The B2Qt build products contains a complete image to be flashed directly to an SD card.
Example usage:
$ sudo umount /dev/sdX* $ zcat tmp/deploy/images/var-som-mx6/b2qt-embedded-qt5-image-var-som-mx6. | sudo dd of=/dev/sdX bs=1M && sync
Replace sdX with the right device name. This can be obtained by "dmesg" command on your host Linux PC, after the SD card reader is inserted.
- Note: Booting your system from an SD card requires pressing the boot-select button, or switching the relevant DIP switch to "Boot from SD card", according to the relevant start-up guide of your system
Drawbacks of the native . b2qt-built image, (relative to the Recovery/Extended SD card):
- The rootfs partition doesn't use the entire SD card.
- The rootfs partition is not labeled as rootfs.
- The NAND flash and eMMC installation scripts and images are not included.
Create an extended SD card
Variscite provides the var-create-yocto-sdcard.sh script which creates our NAND/eMMC recovery SD card. The script copies the NAND/eMMC flash burning scripts and relevant binaries for your convenience.
Later, you will be able to follow Boot2QT Recovery SD card guide to burn your images to NAND flash or eMMC.
Note:
This is essentially the same as our pre-built Recovery SD image, with the following main differences:
- The Android recovery (Android-eMMC) is only present on the pre-built SD image, and not on the SD card built from the Yocto script.
- The pre-built image's rootfs partition size is 3700MiB, which is also the default size when using the script, but the script also has an option to set the rootfs partition size to fill the whole free space of the used SD card. Anyway, you can always resize the partition later with an external tool such as gparted.
Naturally, the pre-built image is more straight forward and easier to use, while the script method is easier to customize.
Usage:
- Follow the Setup and build Yocto guide, and bitbake b2qt-embedded-qt5-image.
- Plug-in the SD card to your Linux HOST PC, run dmesg and see which device is added (i.e. /dev/sdX or /dev/mmcblkX)
$ cd ~/var-b2qt $ sudo MACHINE=var-som-mx6 sources/meta-variscite-fslc/scripts/var_mk_yocto_sdcard/var-create-yocto-sdcard.sh /dev/sdX Replace /dev/sdX with your actual device name, e.g. /dev/sdb
Create an extended SD card image using a loop device
It is also possible to use the var-create-yocto-sdcard.sh script to create an extended SD card image, while using a loop device instead of attaching a real SD card.
$ cd ~/var-b2qt
Create an empty file using the following command:
$ dd if=/dev/zero of=var-som-mx6-extended-sd.img bs=1M count=3720
The above command creates a 3720MiB file representing the SD card.
Attach the first available loop device to this file:
$ sudo losetup -Pf var-som-mx6-extended-sd.img
To find the actual loop device being used, run:
$ losetup -a | grep var-som-mx6-extended-sd.img
Write the content to the loop device to generate the SD card image:
$ sudo MACHINE=var-som-mx6 sources/meta-variscite-fslc/scripts/var_mk_yocto_sdcard/var-create-yocto-sdcard.sh <options> /dev/loopX
(Replace /dev/loopX with your actual loop device, e.g. /dev/loop0)
Detach the loop device from the file:
$ sudo losetup -d /dev/loopX
To compress the SD card image file use the following command:
$ gzip -9 var-som-mx6-extended-sd.img
To write the SD card image to a real SD card device use the following command:
$ zcat var-som-mx6-extended-sd.img.gz | sudo dd of=/dev/sdX bs=1M && sync
(Replace /dev/sdX with your actual SD device, e.g. /dev/sdb)
Boot the board with a bootable SD card
Setting the Boot Mode
Follow the instruction below according to the appropriate carrier board type:
MX6CustomBoard
Booting your MX6CustomBoard system from SD card requires pushing the middle button while powering up the system. See picture below.
To boot a board using an SD card, follow the steps below:
- Power-off the board.
- Insert the SD card into the SD/MMC slot of the carrier board (DVK)
- Push the middle button (Boot Select) and hold
- Power-up the board
- Release the middle button (Boot Select) after system starts to boot.
- The board will automatically boot into Linux from the SD card
SoloCustomBoard
Booting your system requires switching the relevant DIP switch to "Boot from MMC". See picture below.
To boot board with SD card, Follow the steps below:
- Power-off the board.
- Insert the SD card into the SD/MMC slot of the carrier board (DVK)
- Switch the relevant DIP switch to "Boot from MMC"
- Power-up board
- The board will automatically boot into Linux from SD card
DT6CustomBoard
Booting your system requires switching the relevant DIP switch to "Boot from SD card". See picture below.
To boot board with SD card, Follow the steps below:
- Power-off the board.
- Insert the SD card into the SD/MMC slot of the carrier board (DVK)
- Switch the relevant DIP switch to "Boot from SD card"
- Power-up board
- The board will automatically boot into Linux from SD card
Automatic device tree selection in U-Boot
As shown in the Build Results table above, we have different kernel device trees, corresponding to our different H/W configurations.
We implemented a script in U-Boot's environment, which sets the fdt_file environment variable based on the detected hardware.
Enable/Disable automatic device tree selection
To enable the automatic device tree selection in U-Boot (already enabled by default):
$ setenv fdt_file undefined $ saveenv
To disable the automatic device tree selection in U-Boot, set the device tree file manually:
$ setenv fdt_file YOUR_DTB_FILE $ saveenv
Useful example: To list all files in the boot partition (where the dtb files are by default) of an SD card:
$ ls mmc 0:1



