Yocto Programming with Eclipse v2: Difference between revisions
(Copy Yocto_Programming_with_Eclipse) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
tools-debug \ | tools-debug \ | ||
eclipse-debug \ | eclipse-debug \ | ||
ssh-server-openssh \ | |||
" | " | ||
| Line 18: | Line 19: | ||
tcf-agent \ | tcf-agent \ | ||
openssh-sftp-server \ | openssh-sftp-server \ | ||
openssh \ | |||
" | " | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| Line 28: | Line 30: | ||
= Eclipse installation = | = Eclipse installation = | ||
== Download Eclipse == | == Download Eclipse == | ||
Download Eclipse Luna from here: | Download Eclipse Luna from here: https://www.eclipse.org/downloads/download.php?file=/technology/epp/downloads/release/2021-06/R/eclipse-cpp-2021-06-R-linux-gtk-x86_64.tar.gz<br> | ||
Run the following command to unpack and install the downloaded Eclipse IDE tarball into a clean directory using the default name eclipse: | Run the following command to unpack and install the downloaded Eclipse IDE tarball into a clean directory using the default name eclipse: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
$ cd ~ | $ cd ~ | ||
$ tar -xf ~/Downloads/eclipse-cpp- | $ tar -xf ~/Downloads/eclipse-cpp-2021-06-R-linux-gtk-x86_64.tar.gz | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
== Configuring the Eclipse IDE == | == Configuring the Eclipse IDE == | ||
Source the Yocto toolchain script and run the Eclipse IDE with the following commands: | |||
$ cd eclipse | |||
$ source {{#var:TOOLCHAIN_LOCATION}} | |||
$ ./eclipse | |||
Select a new workspace (you can just click OK). | |||
= Create and run a simple application = | = Create and run a simple application = | ||
== Create the Project == | == Create the Project == | ||
You can create | You can create different types of projects: C Managed Build, CMake, Meson, or Makefile-based. This section describes how to create "C Managed Build" projects from within the Eclipse IDE. To create a new project from a "Hello World" template and then display the source code, follow these steps: | ||
* File->New->C Project | * File->New->C/C++ Project | ||
* Click " | * Click "C Managed Build". | ||
* Select "Hello World ANSI C | * Enter a name for the project under the "Project name" field. Do not use hyphens as part of the name. | ||
* Select "Hello World ANSI C Project". | |||
* Select ''Cross GCC'' toolchain | |||
[[File: | [[File:Prj1_V2.jpg]] | ||
* Click "Next". | * Click "Next". | ||
* Add information in the Author field and make sure the License field is correct. | * Add information in the Author field and make sure the License field is correct and click next. | ||
* Accept the default Debug/Release configurations and click next. | |||
* Enter <code>aarch64-fslc-linux-</code> under "Cross compiler prefix" | |||
* Enter <code>/opt/fslc-xwayland/3.1/sysroots/x86_64-fslcsdk-linux/usr/bin/aarch64-fslc-linux</code> under "Cross compiler path" | |||
[[File:Prj1_compiler_V2.jpg]] | |||
* Click "Finish". | * Click "Finish". | ||
* Click on "Workbench". | * Click on "Workbench". | ||
| Line 115: | Line 72: | ||
* Hit Ctrl+B or click the hammer icon to build your project. | * Hit Ctrl+B or click the hammer icon to build your project. | ||
[[File: | [[File:C_perspective_v2.png]] | ||
== Configure Cross Compiler == | |||
In addition to sourcing the yocto environment script, Eclipse must also be configured. Follow these steps to configure sysroot within Eclipse: | |||
* Right click on the project and select ''Properties'' | |||
* Under ''C/C++ Build'', select ''Settings'' | |||
* Add the following flags to ''Miscellaneous'' for ''Cross GCC Compiler'' and ''Cross GCC Linker'' settings: | |||
--sysroot=/opt/fsl-imx-xwayland/5.4-zeus/sysroots/aarch64-poky-linux | |||
[[File:Toolchain_settings.png]] | |||
== | == Configure Remote Debugging == | ||
Using the console of your target set a password with "passwd" command. choose a simple one named "root".<br> | Using the console of your target set a password with "passwd" command. choose a simple one named "root".<br> | ||
The target should be connected to the network via Ethernet or WIFI.<br> | The target should be connected to the network via Ethernet or WIFI.<br> | ||
Use the "ifconfig" command on the target to get its IP address.<br> | Use the "ifconfig" command on the target to get its IP address.<br> | ||
From Eclipse: | From Eclipse: | ||
* | * Click Run->Debug Configurations... | ||
* Double click on ''Remote | * Double click on ''C/C++ Remote Application''. | ||
* Type in a name in the ''Name'' field, such as "hello-world debug remote" | |||
* In the ''Main'' tab, click on ''New...'' to create a new connection. | |||
* In the | |||
[[File: | [[File:GDB_Conn.png]] | ||
* | * Select ''SSH'' for the connection type and click ''OK''. | ||
* Enter the Target IP Address. | |||
* Enter ''root'' for the user. | |||
* Change to "Password based authentication" and enter password configured in previous step. | |||
* | * Click ''Finish'' | ||
* | * Type "/home/root/hello-world" in the ''Remote Absolute File Path for C/C++ Application'' field | ||
* Enter | * Click on the ''Debugger'' tab | ||
* Enter "aarch64-fslc-linux-gdb" in the ''GDB debugger'' field | |||
[[File:GDB_Conn_2.png]] | |||
* Click ''Apply'' and ''Close'' to finish configuring the debugger | |||
== Remote debug == | == Remote debug == | ||
| Line 146: | Line 112: | ||
Follow the below steps to remotely debug your application on the {{#var:HARDWARE_NAME}}. | Follow the below steps to remotely debug your application on the {{#var:HARDWARE_NAME}}. | ||
* | * Use the keyboard shortcut ''ctrl-b'' to rebuild the application. | ||
* | * Click the bug icon in the toolbar and select "hello-world debug remote" (or whichever name you supplied in the previous step) | ||
* Follow the prompt to switch to the Debug perspective | |||
* | |||
[[File:Dbg2_v2.png]] | |||
[[File: | |||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
You can now run and debug your program via eclipse. The actual program execution is done on the target, and the output is seen on the Remote Shell on Eclipse. | You can now run and debug your program via eclipse. The actual program execution is done on the target, and the output is seen on the Remote Shell on Eclipse. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Revision as of 21:23, 16 July 2021
This guide describes how to use Eclipse to develop and debug applications on the DART-6UL.
Create your rootfs with Eclipse debug support
Append the following to the conf/local.conf file in your Yocto build directory:
EXTRA_IMAGE_FEATURES = " \
debug-tweaks \
tools-debug \
eclipse-debug \
ssh-server-openssh \
"
IMAGE_INSTALL_append = " \
tcf-agent \
openssh-sftp-server \
openssh \
"
Now bitbake your image.
Host tools
To install the toolchain follow Yocto Toolchain installation guide.
Eclipse installation
Download Eclipse
Download Eclipse Luna from here: https://www.eclipse.org/downloads/download.php?file=/technology/epp/downloads/release/2021-06/R/eclipse-cpp-2021-06-R-linux-gtk-x86_64.tar.gz
Run the following command to unpack and install the downloaded Eclipse IDE tarball into a clean directory using the default name eclipse:
$ cd ~ $ tar -xf ~/Downloads/eclipse-cpp-2021-06-R-linux-gtk-x86_64.tar.gz
Configuring the Eclipse IDE
Source the Yocto toolchain script and run the Eclipse IDE with the following commands:
$ cd eclipse $ source /opt/fslc-x11/2.2.1/environment-setup-armv7at2hf-neon-fslc-linux-gnueabi $ ./eclipse
Select a new workspace (you can just click OK).
Create and run a simple application
Create the Project
You can create different types of projects: C Managed Build, CMake, Meson, or Makefile-based. This section describes how to create "C Managed Build" projects from within the Eclipse IDE. To create a new project from a "Hello World" template and then display the source code, follow these steps:
- File->New->C/C++ Project
- Click "C Managed Build".
- Enter a name for the project under the "Project name" field. Do not use hyphens as part of the name.
- Select "Hello World ANSI C Project".
- Select Cross GCC toolchain
- Click "Next".
- Add information in the Author field and make sure the License field is correct and click next.
- Accept the default Debug/Release configurations and click next.
- Enter
aarch64-fslc-linux-under "Cross compiler prefix" - Enter
/opt/fslc-xwayland/3.1/sysroots/x86_64-fslcsdk-linux/usr/bin/aarch64-fslc-linuxunder "Cross compiler path"
- Click "Finish".
- Click on "Workbench".
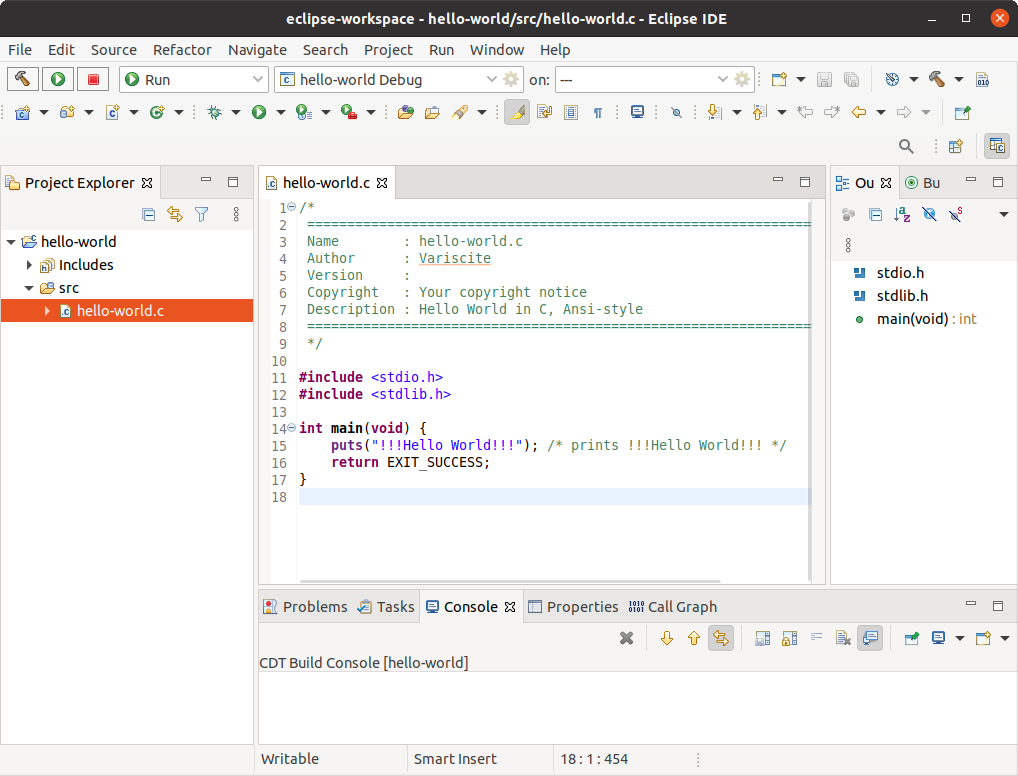
- You should now be in the C/C++ perspective. The left-hand navigation pane shows your project. You can display your source by double clicking the project's source file.
- Hit Ctrl+B or click the hammer icon to build your project.
Configure Cross Compiler
In addition to sourcing the yocto environment script, Eclipse must also be configured. Follow these steps to configure sysroot within Eclipse:
- Right click on the project and select Properties
- Under C/C++ Build, select Settings
- Add the following flags to Miscellaneous for Cross GCC Compiler and Cross GCC Linker settings:
--sysroot=/opt/fsl-imx-xwayland/5.4-zeus/sysroots/aarch64-poky-linux
Configure Remote Debugging
Using the console of your target set a password with "passwd" command. choose a simple one named "root".
The target should be connected to the network via Ethernet or WIFI.
Use the "ifconfig" command on the target to get its IP address.
From Eclipse:
- Click Run->Debug Configurations...
- Double click on C/C++ Remote Application.
- Type in a name in the Name field, such as "hello-world debug remote"
- In the Main tab, click on New... to create a new connection.
- Select SSH for the connection type and click OK.
- Enter the Target IP Address.
- Enter root for the user.
- Change to "Password based authentication" and enter password configured in previous step.
- Click Finish
- Type "/home/root/hello-world" in the Remote Absolute File Path for C/C++ Application field
- Click on the Debugger tab
- Enter "aarch64-fslc-linux-gdb" in the GDB debugger field
- Click Apply and Close to finish configuring the debugger
Remote debug
Follow the below steps to remotely debug your application on the DART-6UL.
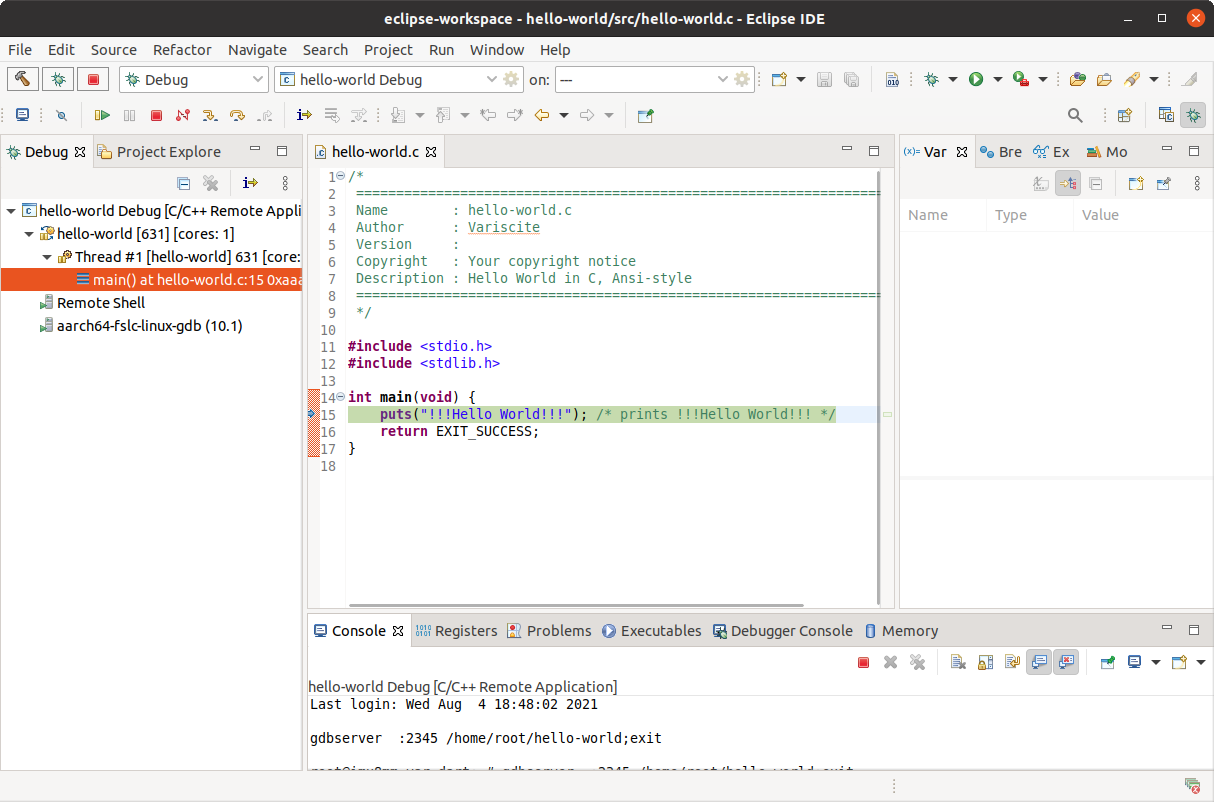
- Use the keyboard shortcut ctrl-b to rebuild the application.
- Click the bug icon in the toolbar and select "hello-world debug remote" (or whichever name you supplied in the previous step)
- Follow the prompt to switch to the Debug perspective
You can now run and debug your program via eclipse. The actual program execution is done on the target, and the output is seen on the Remote Shell on Eclipse.